Introduction
AI chatbots have transformed customer interactions, business automation, and digital experiences. However, many chatbots still feel robotic, impersonal, or frustrating due to a lack of emotional intelligence, contextual understanding, and natural conversation flow. The key to success is making chatbots feel more human-like by enhancing their ability to understand emotions, adapt responses, and engage users in meaningful conversations.
With advances in GPT-4 and beyond, chatbots are becoming more sophisticated, but building a truly human-like chatbot requires more than just AI—it requires designing experiences that feel natural, intuitive, and emotionally intelligent. In this blog, we’ll explore the best practices for building AI chatbots that feel more human, the advantages of doing so, and how different industries can leverage them.
Why Do Human-Like Chatbots Matter?
✅ Better User Engagement – People prefer conversations that feel natural and friendly.
✅ Higher Customer Satisfaction – Users feel more valued when a chatbot understands their emotions.
✅ Increased Retention & Loyalty – A positive chatbot experience encourages users to return.
✅ More Effective Problem-Solving – Human-like chatbots understand nuances and provide relevant answers.
✅ Seamless Business Integration – A natural chatbot experience reduces friction in customer support and sales.
Best Practices for Building Human-Like AI Chatbots
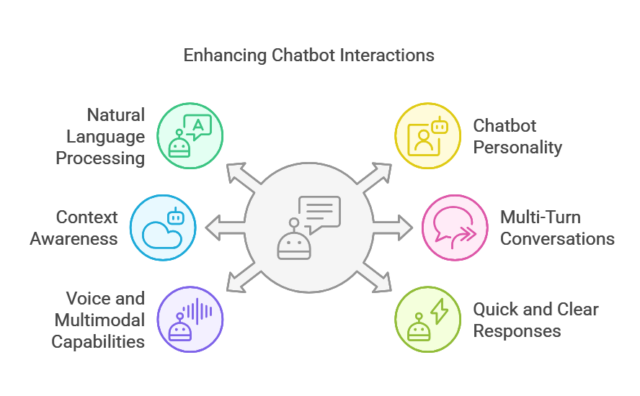
1. Use Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Real Conversations
- Implement advanced NLP models like GPT-4 to understand user intent and respond contextually.
- Train your chatbot to handle typos, slang, and variations of phrases to make conversations feel more organic.
- Use sentiment analysis to adjust tone and responses based on user emotions.
2. Give Your Chatbot a Personality
- Define a chatbot persona that aligns with your brand (e.g., friendly, professional, humorous).
- Use consistent tone and vocabulary to create a natural interaction.
- Add personal touches like greetings, humor, and small talk to make conversations feel less robotic.
3. Implement Context Awareness & Memory
- Use AI models that remember previous conversations to avoid repetitive responses.
- Enable context awareness so that the chatbot understands follow-up questions.
- Example: If a user asks, “What’s the weather like in New York?” and follows up with, “What about tomorrow?”, the chatbot should retain the context.
4. Support Multi-Turn Conversations
- Design the chatbot to handle complex conversations rather than just answering one-off queries.
- Ensure the chatbot can guide users through step-by-step processes like troubleshooting, booking appointments, or making purchases.
5. Use Voice and Multimodal Capabilities
- Integrate voice-based AI for a more interactive experience (e.g., Siri, Google Assistant).
- Leverage multimodal AI to process text, images, and videos for enhanced communication.
- Example: A chatbot helping with tech support could allow users to upload screenshots of their issue for better assistance.
6. Provide Quick & Clear Responses
- Avoid long, robotic-sounding paragraphs. Keep responses concise and engaging.
- Use short sentences, bullet points, and simple language to improve clarity.
- Example: Instead of saying, “We acknowledge your request and will proceed accordingly,” say, “Got it! I’ll take care of that for you.”
7. Add Human-like Delays & Typing Indicators
- Instant responses feel unnatural. Add a slight delay to simulate human response time.
- Use typing indicators (“…” like in messaging apps) to create a conversational experience.
8. Use Empathy & Emotional Intelligence
- Recognize user emotions using sentiment analysis and adjust responses accordingly.
- If a user expresses frustration, respond with empathy:
- ❌ “I don’t understand your request.”
- ✅ “I’m sorry to hear that. Let me help you fix this.”
9. Provide the Option to Connect with a Human
- A chatbot should not replace human support but complement it.
- Offer users the option to speak with a live agent when needed.
- Example: “Would you like to chat with one of our support specialists?”
10. Continuous Learning & Improvement
- Use machine learning to improve chatbot responses based on user interactions.
- Regularly analyze chatbot logs and feedback to fine-tune conversations.
- Train the chatbot to handle new trends, slang, and evolving customer queries.
How to Implement a Human-Like Chatbot
Step 1: Define Objectives & Audience
- Determine the chatbot’s purpose (e.g., customer support, lead generation, automation).
- Identify the target audience and common queries they may ask.
Step 2: Choose the Right AI Model
- Use GPT-4 API, Dialogflow, Rasa, Microsoft Bot Framework, or OpenAI’s ChatGPT for NLP-based chatbots.
- Select text, voice, or multimodal capabilities based on user needs.
Step 3: Design Conversational Flows
- Map out realistic conversations based on user queries.
- Implement error-handling and fallback responses to avoid dead-ends.
Step 4: Personalize & Train the Chatbot
- Train the chatbot with industry-specific data and real user conversations.
- Enable user memory retention for personalized responses.
Step 5: Test, Deploy & Optimize
- Conduct A/B testing to compare different chatbot responses.
- Use analytics and user feedback to improve conversation quality.
- Continuously update and refine chatbot interactions.
Industries Benefiting from Human-Like Chatbots
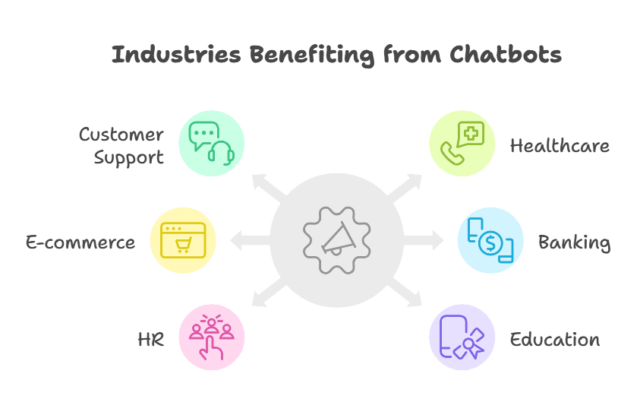
1. Customer Support & Service
- Reduces wait times and handles common queries automatically.
- Example: AI-powered support chatbots for banking and telecom.
2. Healthcare & Telemedicine
- Provides 24/7 patient support, appointment scheduling, and symptom checking.
- Example: Virtual health assistants like Woebot for mental health.
3. E-commerce & Retail
- Recommends products, helps with orders, and answers FAQs.
- Example: AI shopping assistants on Amazon & Shopify.
4. Banking & Finance
- Automates transactions, detects fraud, and provides investment advice.
- Example: AI-driven financial advisors and fraud detection bots.
5. HR & Recruitment
- Screens candidates, schedules interviews, and handles onboarding.
- Example: Chatbots for automated recruitment processes.
6. Education & E-Learning
- Personalized learning assistants help students with coursework.
- Example: AI tutors on platforms like Duolingo and Coursera.
7. Travel & Hospitality
- Assists with bookings, travel plans, and hotel reservations.
- Example: AI travel concierge services.
8. Real Estate
- Provides property recommendations, pricing insights, and virtual tours.
- Example: AI-driven real estate assistants.
9. Government & Public Services
- Handles citizen inquiries, document processing, and service requests.
- Example: GovChat AI for answering public queries.
10. Marketing & Lead Generation
- Engages visitors, qualifies leads, and increases conversions.
- Example: Automated marketing chatbots for websites and social media.
Conclusion
Building AI chatbots that feel more human-like requires advanced NLP, emotional intelligence, and seamless conversation design. GPT-4 and future AI models provide the foundation, but the key is to create experiences that are engaging, empathetic, and intuitive. Whether for customer service, healthcare, e-commerce, or finance, human-like chatbots improve user engagement, boost business efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
🚀 Are you ready to build a chatbot that truly feels human? Start implementing these best practices today!
